In the previous article, we define questionnaire as a directed acyclic graph (DAG). In this article, we will look into how versioning can be done on a DAG.
Versioning
With versioning, we are able to keep track of changes, and revert back to specific version of the questionnaire. This means the questionnaire must be immutable.
This comes to the term: Persistent data structure. A persistent data structure is a data structure that always preserves the previous version of itself when it is modified.
There are different approaches to make data structure persistent. The no-brainer way would be cloning the whole questionnaire and make changes on the cloned one. Apparently this approach wastes a lots of storage, and it is not efficient as well.
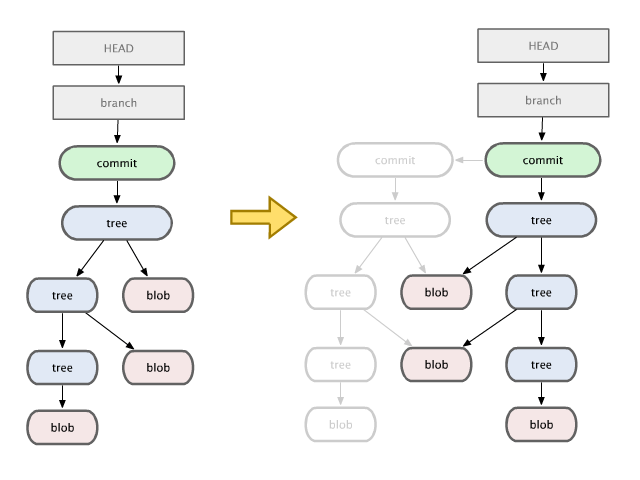
Although it may not be relevant to our case, it is interesting to learn how Git manages repositories. Git Object Model is essentially a Persistent Tree. When we want to update a node (or a file in repository), we make a copy of the node, and cascade the change to ancestor nodes of the tree until reaching the root, causing chain of updates. The details are explained here.
In our case, we are going to adopt something similar to Time-based Versioning. The graph is versioned by Timestamp.
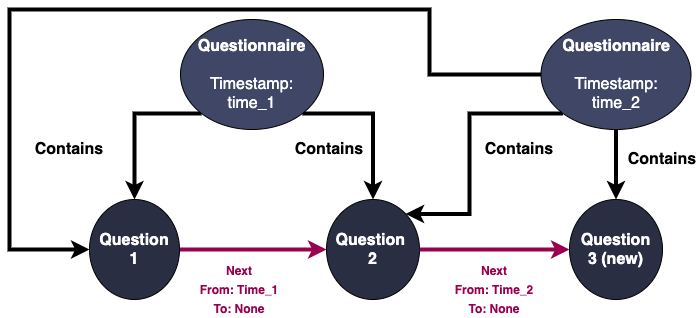
Creation
For Next relationship, we introduce 2 properties: From and to, representing the time interval that the relationship is valid. If to equal to None, that means it is still currently valid.
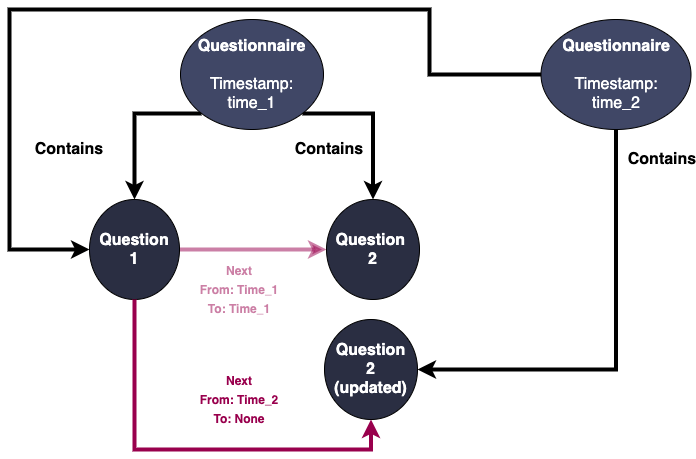
Update
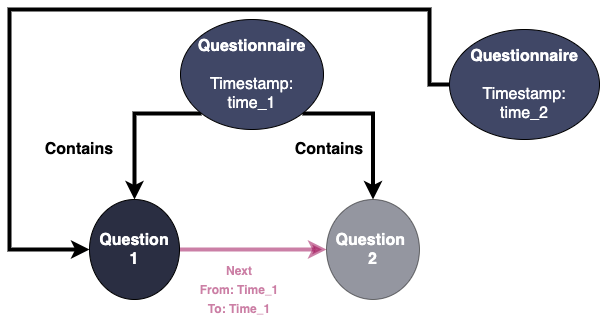
Deletion
Questions become immutable now. We can trace back to target version through specific Timestamp. Nice!